Once you’ve confirmed that your product idea is viable (through market research and competitor analysis), It’s time to sit down and plan out the core features of your application.
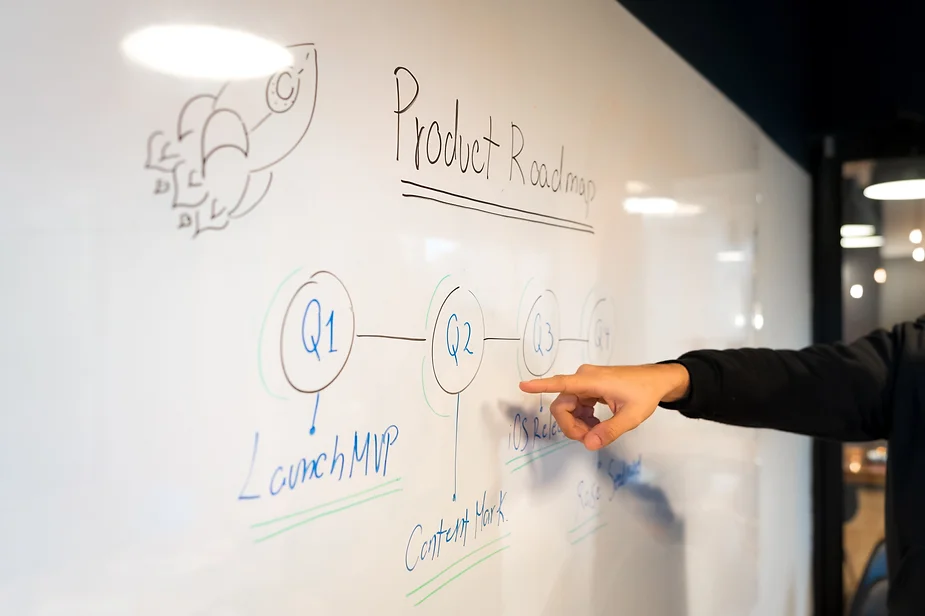
The planning and development of an MVP are strongly intertwined. Development is a lot easier if you do the legwork during the planning stage; you simply follow the plan.
The root problem, however, is a lack of awareness of the steps involved in the MVP development process. To construct an MVP successfully, you must complete all of the processes described below:
Conduct AN INITIAL MARKET ANALYSIS
Ideas don’t always meet the market’s requirements. Before starting the MVP development process, a company should make sure that the idea meets the demands of the intended users. This can be performed through the use of surveys. At the end of the day, the more data a company has, the better its chances of succeeding.
There’s a chance you’ll come up with the same idea as someone else in the market. Given the existence of so many people in the world, certain concepts are destined to be repetitive. Although similar ideas aren’t a problem, their potential and viability should be examined.
DEFINE YOUR PRODUCT’S UNIQUENESS —
The main goal is to create a product that will attract customers who will eventually utilize it because of particular features that set it apart from the competition. Knowing what makes your app stand out from the start can help you focus your efforts (both time and money) from the start.
It should also be obvious what the product’s critical estimations are. As the term “minimum viable product” implies, the product must provide value to users in its most basic form. Begin by drawing out the users’ requirements and then building the MVP around them.
Create User Flow Diagram
The design stage of the MVP is crucial.
Design the app in a way that is user-friendly. The company must consider the app from the user’s point of view, from the first time they open it to the final process, Furthermore, user flow is an important factor to consider because it ensures that nothing is neglected while keeping the future product and its users in mind. The process steps must be defined before the user flow can be defined. It is critical to explain the steps required to achieve the main goal in this relationship. Rather than focusing on features, the focus should be on basic tasks such as finding and purchasing the product or managing and receiving orders.
These are the goals that the end-users will have while using the product. It’s time to specify the features of each stage after each of these procedure stages has been properly put out.
MVP Features Should Be Prioritized
Divide the list into the most important features and features that can be added after the MVP is released. Examine everything as thoroughly as possible until you have a filtered and organized list based on your understanding of market objectives and requirements.
Another crucial step is to organize these features in the backlog of the product (priority-wise). It’s time to start creating an MVP. An MVP prototype can be created if a company wishes to see how their future product will look.
REVIEW THE CORE FEATURES WITH YOUR TEAM AND LAUNCH YOUR MVP —
This step requires more knowledge because you’ll go over the list of features with your team and look at the development side to come up with estimates of time and costs for each feature, giving you the final say in which ones to include in your MVP.
The MVP can be created once a company has decided on the main features and has learned about market needs. Keep in mind that an MVP is not a lower-quality version of the final product; it must still meet the needs of the customer. As a result, it must be simple to use, entertaining, and appropriate for the users.
The main advantage of an MVP is that it allows you to assess your user’s interest before committing resources to the product. The sooner you can determine whether your product will appeal to clients, the less time and money you’ll waste on a product that won’t sell. After launching the MVP, go over everything again. That is, the company must get feedback from its customers on the release. They can determine the acceptance and competitiveness of their goods in the market based on their comments.